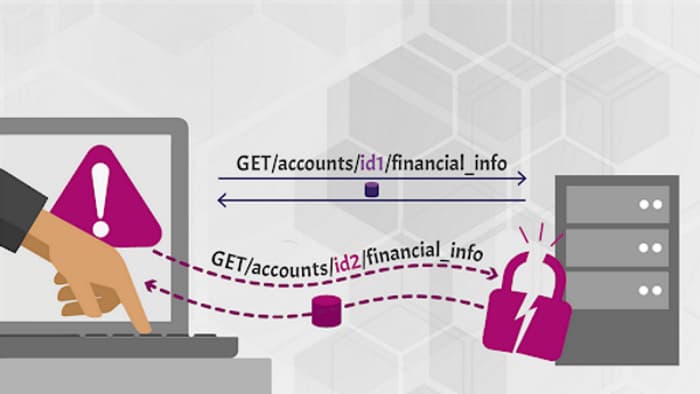
Attackers substitute the ID of their own resource in the API call with an ID of a resource belonging to another user. The lack of proper authorization checks allows attackers to access the specified resource. This attack is also known as IDOR (Insecure Direct Object Reference).
Use case
- API call parameters use the ID of the resource accessed through the API
/api/shop1/financial_info. - Attackers replace the IDs of their resources with a different one which they guessed through
/api/shop2/financial_info. - The API does not check permissions and lets the call through.
- Problem is aggravated if IDs can be enumerated
/api/123/financial_info.
How to prevent
- Implement authorization checks with user policies and hierarchy.
- Do not rely on IDs that the client sends. Use IDs stored in the session object instead.
- Check authorization for each client request to access database.
- Use random IDs that cannot be guessed (UUIDs).